Retail insurance brokers are a vital distribution channel for insurers, particularly in personal lines and small and midsize enterprise coverage. However, industry consolidation, digitization, and rising customer expectations are rapidly reshaping the brokerage landscape. Brokers now must manage larger, more diverse portfolios, deliver differentiated value to clients, and adapt quickly to shifting market dynamics.
This evolving environment creates significant opportunities for insurers. By providing targeted, tailored support to brokers, insurers can become indispensable allies in navigating the market’s growing complexity. Insurers that align their services, solutions, and digital tools with brokers’ needs can build stronger relationships, capture a greater share of brokers’ business, and secure access to promising growth segments.
To seize these opportunities, insurers must understand the structural shifts reshaping the brokerage industry and determine how to maximize the value of their support to brokers. By delivering targeted support—through more focused engagement, tailored product offerings, modernized technology systems, and responsive service delivery, for example—insurers can position themselves as strategic partners and foster enduring relationships.
Seven Strategic Levers to Build Broker Relationships
Our experience in client engagements has consistently highlighted seven common challenges in the evolving brokerage landscape. (See Exhibit 1.) Insurers can apply the following strategic levers to address these challenges and win in the retail broker channel.
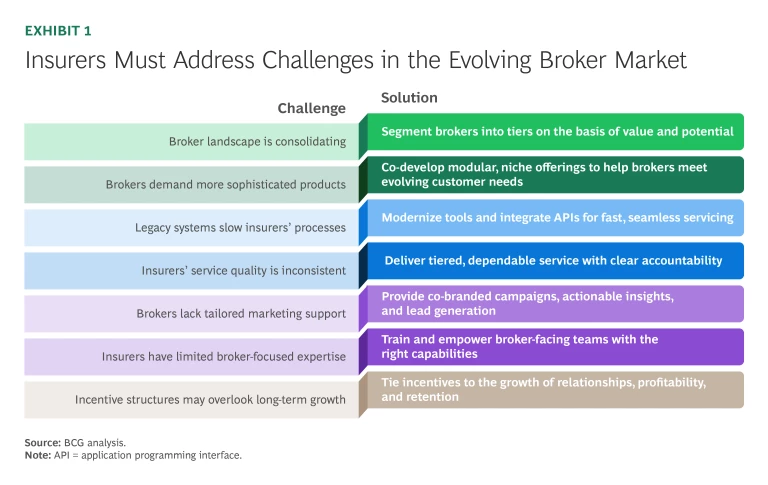
Sharpening Focus in a Consolidating Market. The retail broker landscape is consolidating, creating fewer but larger and more sophisticated broker organizations. These leading firms wield greater negotiating power, have higher expectations for service quality, and seek highly customized solutions. At the same time, a diverse array of smaller brokers continues to serve specialized markets, each confronting unique challenges and resource limitations.
Despite these distinctions, many insurers still employ a uniform approach when engaging with brokers. This one-size-fits-all strategy results in operational inefficiencies, underperformance with strategically important brokers, and missed opportunities for growth.
To sharpen their focus, insurers should classify brokers into tiers based on criteria such as premium volume, profitability, and strategic alignment. Top-tier brokers should receive dedicated account managers and prioritized service, ensuring these high-value relationships get the necessary resources. Insurers should leverage relevant KPIs (for example, net new premiums generated) to regularly reassess and update broker tiers, reallocating services to reflect market realities and strategic goals.
Collaborating to Offer Tailored Insurance Solutions. End customers in the retail channel—individuals and small and midsize enterprises—increasingly seek tailored, customizable insurance coverage.
To capitalize on the valuable opportunity created by this trend, insurers should partner with brokers to co-develop modular, adaptable products tailored to changing client preferences. Insurers can also support top-tier brokers by offering distinctive coverage enhancements or specialized products, enabling brokers to stand out in competitive markets. Additionally, insurers can provide specialized support, such as cyber coverage expertise, to help brokers capture emerging customer segments and stay ahead of industry trends.
Modernizing Systems to Meet Broker Expectations. Today’s brokers expect fast, streamlined interactions. If insurers fail to deliver, brokers may shift their business elsewhere. Yet insurers’ manual processes and legacy IT systems used in quoting, underwriting, claims-handling, and servicing can create significant friction for brokers.
To meet expectations, insurers must modernize their technology infrastructure. Implementing real-time quoting capabilities, integrating IT systems using application programming interfaces (APIs), and automating underwriting processes can improve responsiveness. Additionally, insurers should develop intuitive broker portals with robust self-service capabilities, allowing brokers to quickly issue policies, track claims, and manage service requests. Streamlining workflows in this way boosts operational efficiency for both insurers and brokers and enhances broker satisfaction.
Ensuring Consistent and Reliable Broker Support. Variable service delivery across regions and teams creates unpredictability for brokers, weakens trust, and undermines insurers’ credibility. Inconsistent touch points and lengthy turnaround times frustrate brokers, potentially driving them to competitors.
To provide brokers with a consistently high-quality experience, insurers should determine and reliably meet the appropriate service level for each broker tier. Broker-specific training programs should also be implemented to ensure consistency on risk appetites and underwriting standards. Additionally, insurers should designate dedicated claims managers for high-value brokers to expedite claims resolutions.
Developing Targeted Marketing and Communications. Brokers value practical insights and effective marketing tools that help them expand their business. Yet insurers often do not provide brokers with sufficiently targeted marketing support and practical tools, missing opportunities to help brokers effectively grow their client base.
To improve broker relationships and promote mutual growth, insurers can collaborate with brokers on co-branded or exclusive marketing campaigns that enhance brokers’ visibility in their markets—while respecting regulatory standards and best practices. Insurers can also share targeted data insights and analytics on market trends and promising client segments. Additionally, insurers should develop lead-generation tools and referral programs designed to attract new clients for both parties.
Enhancing Broker-Related Expertise. Insurers’ internal teams often face talent and knowledge gaps that limit their ability to fully embrace a broker-centric go-to-market model. Without dedicated expertise and an understanding of brokers’ unique challenges and objectives, insurers struggle to consistently deliver the high-quality service brokers increasingly expect.
To effectively close these gaps, insurers should train and deploy specialized broker relationship managers who understand broker operations and business strategies. They should also realign internal processes to enable rapid responses to broker needs, encouraging greater collaboration across functions. Finally, insurers should prioritize ongoing training and skill development so that their internal teams have the agility and knowledge to respond to their brokers’ evolving demands.
Aligning Incentive Structures. Many insurers rely on internal KPIs that reward meeting short-term sales goals rather than establishing long-term, collaborative broker partnerships. This misalignment inadvertently de-emphasizes service quality and broker satisfaction, ultimately limiting an insurer’s share of brokers’ business.
To correct this misalignment, insurers should adopt performance-based compensation that ties incentives to the growth of relationships, profitability, and retention. In addition, transparent, multiyear reward programs can encourage brokers to maintain enduring relationships. Insurers should also foster a culture in which broker satisfaction is a core KPI, ensuring alignment across sales, underwriting, and support functions.
Assessing the Maturity of Broker Servicing
Insurers should adopt a structured approach to assessing their broker-servicing maturity, identifying pain points and opportunities across their broker engagement model. A comprehensive assessment spans the seven topics covered by the strategic levers:
- Segmentation and Broker Rating. Do our segmentation and rating approaches allow us to focus on the right brokers and allocate resources on the basis of brokers’ performance levels and growth potential?
- Customer Solutions. Do the solutions that we provide for brokers allow us to maximize opportunities in the broker market? Do we make our risk appetite clear to brokers and provide flexible solutions to an appropriate extent?
- Processes and Systems. Do our processes and systems let us interact with brokers efficiently? Do these processes leverage technology, such as process automation and standardized APIs? Do we have a comprehensive view of brokers and customers across our lines of business?
- Support and Service. Do we currently consider brokers’ service needs? Do we offer the right services and adjust service levels to brokers’ performance levels and growth potential?
- Marketing and Market Development. Do our governance processes and structures allow us to identify market opportunities and set clear strategies for market development? Do marketing efforts support brokers appropriately? Do we provide the right sales toolkits?
- Broker-Focused Operations. Do our practices and operational processes help us manage our brokers effectively? Are our broker-facing teams adequately staffed, trained, and empowered to deliver consistently high-quality broker service?
- Incentive Structures. Do our internal KPIs and incentive programs prioritize long-term broker relationships alongside short-term results? Are compensation structures aligned with broker profitability, growth, and retention?
The Assessment in Action: Comparing Archetypes
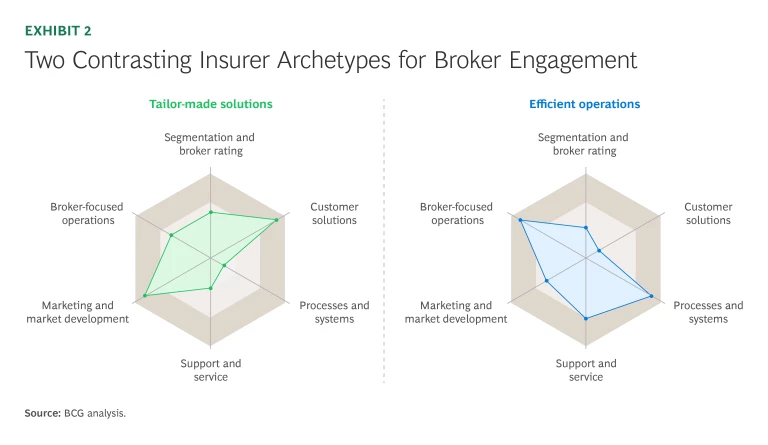
With insights from a maturity assessment, insurers can identify critical gaps in segmentation, service quality, systems efficiency, and other key areas, and design targeted solutions to address them. In our recent assessments, we have frequently seen two contrasting insurer archetypes among the many possible approaches to broker engagement, each entailing distinctive challenges and solutions. (See Exhibit 2.)
- Tailor-Made Solutions. Insurers in this archetype provide highly customized solutions and extensive marketing support tailored precisely to broker requests. Although brokers value this bespoke approach, the resulting complexity overwhelms insurers’ operational processes and systems, especially affecting service to their network of smaller brokers. To enable customization without hindering efficiency, successful insurers develop a set of modular product offerings for brokers and redesign processes to facilitate speed and customization.
- Efficient Operations. These insurers emphasize efficiency and standardized processes, enabling consistent and cost-effective servicing. However, brokers often view the approach as overly rigid, limiting growth opportunities. Recognizing this barrier, some insurers have strategically introduced controlled flexibility into their processes and empowered broker-facing teams to accommodate special needs or requests for select brokers. This allows insurers to better align their service to brokers’ expectations without sacrificing their operational efficiency.
By systematically assessing their maturity in broker servicing and understanding the spectrum of possible engagement archetypes, insurers can create a clear, actionable roadmap to guide a large-scale implementation of the seven strategic levers.
To effectively address broker engagement challenges in today’s evolving landscape, insurers must adopt a targeted, data-driven strategy. By focusing their engagement efforts, delivering tailored products and services, investing in modern systems and processes, and aligning incentives, insurers can strengthen broker relationships and loyalty. Those insurers that proactively embrace these actions will not only capture greater market share but also position themselves as trusted, indispensable partners—unlocking sustainable growth and competitive advantage through the broker channel.






