Imagine having a personal shopper who deeply understands your preferences, lifestyle, and budget, effortlessly curating tailored product recommendations from thousands of options. Your shopper seamlessly anticipates your needs, secures the best prices, and completes transactions autonomously—transforming shopping from a chore into an engaging and delightful experience.
What’s more, that shopper isn’t human. It’s an AI agent.
Welcome to the era of agentic commerce, where a retailer’s most valuable customer might not be a human. AI agents—embedded in platforms like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini—are increasingly influencing consumers’ decisions, redefining how they discover, evaluate, and purchase products online. Without intervention, retailers risk being reduced to background utilities in agent-controlled marketplaces.
The rise of AI shopping agents represents a seismic shift in how commerce will be conducted on a global scale—and it’s already underway. More than half of consumers anticipate using AI assistants for shopping by the end of 2025, according to Adobe. But this is more than just a story of adoption—customers arriving via AI agents are 10% more engaged than traditional visitors, reaching retailers further down the sales funnel with a stronger intent to purchase.
For retailers, however, the risks are clear: diminished direct access to customers, weaker brand loyalty, and a growing dependence on intermediary platforms.
Stay ahead with BCG insights on the consumer products industry
Staying competitive will require more than incremental change. Retailers must fight to reclaim relevance—by asserting their presence within AI ecosystems, launching proprietary agents that showcase their brand’s unique edge, and building the technical and organizational foundations to operate at AI speed and scale. This is not a future-state ambition—it’s a strategic imperative today that many retailers are not yet prepared to meet.
The Rise of Agentic Commerce
AI shopping agents are redefining digital commerce by automating tasks that once required active consumer effort. Instead of consumers manually searching, comparing, and deciding, agents can scan several platforms, filter results against individual preferences, compare features and prices, and make context-aware recommendations.
As trust in these systems grows, agents will increasingly take on transactional tasks—checking delivery timelines, applying stored payment credentials, and completing purchases autonomously. (See Exhibit 1.) This shift will streamline the path to purchase, reduce friction, and enable a seamless, conversational shopping experience that requires minimal human input.
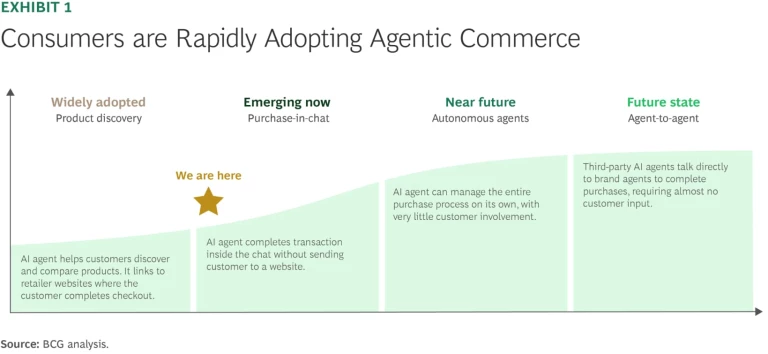
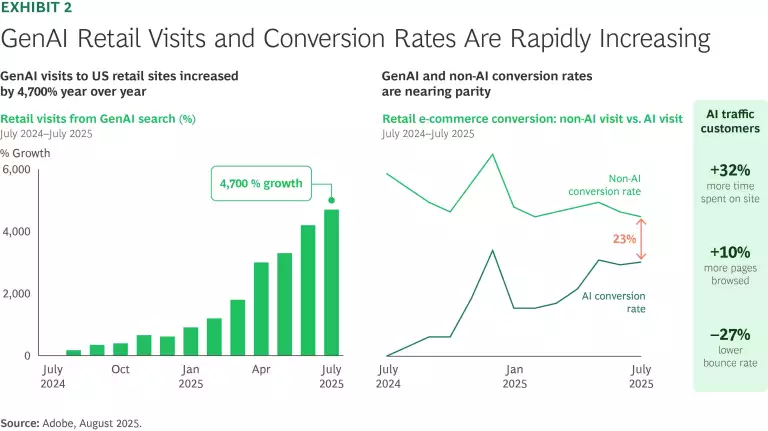
Consumer adoption of agentic shopping technologies is increasing quickly. Traffic to US retail sites from GenAI browsers and chat services increased 4,700% year-over-year in July 2025, according to Adobe. And these users are engaging more deeply: they spend 32% more time on the site, browse 10% more pages, and have a 27% lower bounce rate. (See Exhibit 2.)
Major industry players like Perplexity, ChatGPT, and Google Gemini are rapidly embedding comprehensive commerce functionalities into their AI platforms, intensifying competition and further accelerating the transformation.
Perplexity has moved particularly fast. The company initially launched “Buy with Pro,” allowing users to browse products and complete one-click purchases directly from select merchants. It subsequently integrated Firmly.ai, a behind-the-scenes connector that allows merchants to easily link to Perplexity, thus expanding the assortment available for in-platform checkout. It also partnered with PayPal to roll out secure, streamlined checkout directly within the chat interface.
ChatGPT is advancing on multiple fronts as well, including the recent introduction of “Instant Checkout.” This new feature enables customers to complete purchases directly within the chat window—seamlessly moving from product discovery to payment. The rollout is starting with Etsy merchants, with plans to extend to Shopify merchants in the near future.
Meanwhile, Google announced that it will expand its AI Mode shopping interface in the US, adding advanced agentic capabilities in the coming months. Today, AI Mode lets customers browse and compare products. The new update will enable them to track prices and confirm purchases directly within the platform. Once the purchase is confirmed, the transaction will be completed on their behalf via Google Pay.
The Threats to Retailers
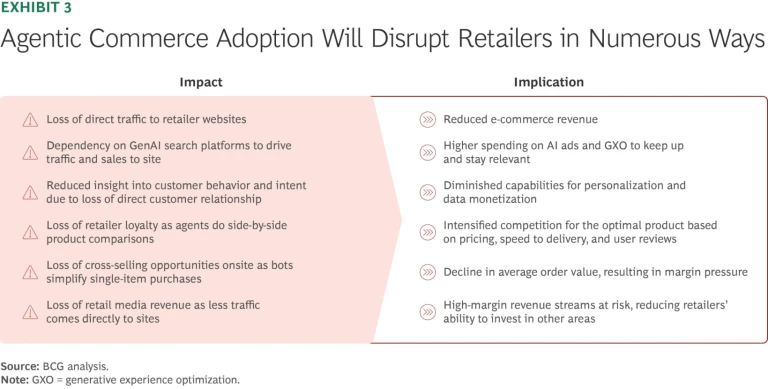
The advancements in agentic shopping present substantial challenges for traditional retailers, primarily through risks associated with disintermediation—when retailers are bypassed in favor of AI platforms that complete the entire shopping journey outside of the retailer's e-commerce platform. As GenAI platforms become the default entry point for online shopping, consumers increasingly bypass retailer websites. The growth of zero-click search and agent-driven interactions is eroding direct traffic—along with the retailer's ability to observe, influence, and understand consumer behavior at scale.
The growth of zero-click search and agent-driven interactions is eroding direct traffic—along with the retailer's ability to observe, influence, and understand consumer behavior at scale.
Moreover, agents can behave differently from human shoppers: they prioritize price, user ratings, delivery speed, and real-time inventory over brand familiarity or loyalty. This has the potential to reshape how retailers compete and how purchase decisions are made.
This shift has far-reaching consequences. (See Exhibit 3.) Retailers will become increasingly dependent on third-party AI ecosystems to drive visibility and conversion, while losing access to first-party data that powers personalization, loyalty, and monetization. At the same time, AI agents’ emphasis on utility weakens traditional brand loyalty, limits cross-selling opportunities, and puts retail media revenues under pressure, all while intensifying the race to the bottom on price and delivery speed.
Most global retailers recognize that they must respond to the shifting landscape. Among those retailers surveyed by monday.com, almost all (96%) report they are exploring or implementing AI agents. More than two-thirds (68%) believe that in five years, AI agents will handle most of their customer interactions, while nearly two-thirds (63%) agree that companies that do not adopt AI agents risk falling behind in the next two years.
How Retailers Can Prevail in This New Normal
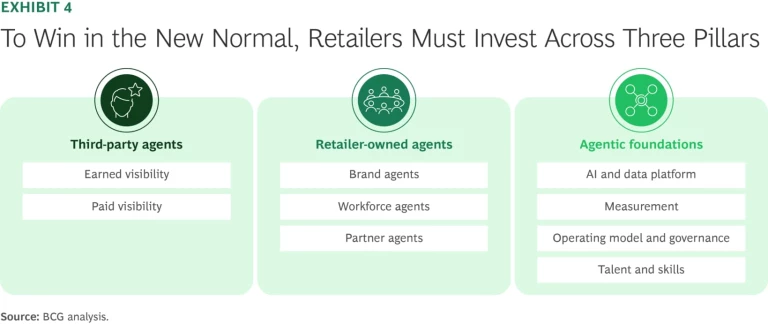
To navigate these challenges, retailers must reimagine customer engagement while embracing AI technologies. An effective strategy entails investing across three pillars. (See Exhibit 4.)
1. Winning with Third-Party Agents
To remain competitive as third-party AI agents gain influence, retailers need to ensure discoverability by enhancing earned visibility and capitalizing on emerging paid advertising opportunities.
Earned Visibility. The traditional approach of search engine optimization (SEO) is giving way to generative experience optimization (GXO), a strategy that enhances content for AI-driven interactions. (See Exhibit 5.)
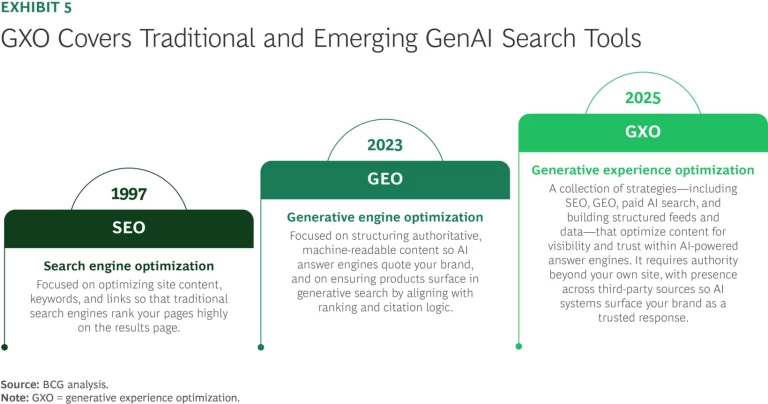
As a prerequisite for GXO, retailers must invest in AI-ready content operations: structuring data and assets so they are authoritative, semantically rich, factual, and machine-readable. Retrieval-augmented generation systems depend on this type of content to ingest, cite, and rank sources. Success will require continuous, modular production that enables generative engines to surface brand and product information in answers and recommendations.
Structured content is not enough. Generative engines increasingly prioritize insights drawn from social and community platforms like Reddit, Wikipedia, YouTube, and Quora, which means that retailers and brands must also build and maintain a presence across the wider digital ecosystem. By engaging on these influential platforms, they increase the likelihood that AI models recognize, reference, and ultimately trust their content.
Together, these elements define the transition from SEO to GXO: a shift to optimizing for AI-driven answers, recommendations, and transactions as generative engines evolve into decision engines.
Paid Visibility. As SEO gives way to GXO, generative paid media is emerging—though its shape is still evolving. Early formats—including Google’s AI Max, Perplexity’s sponsored questions, and Grok’s in-chat advertising—already signal what’s to come.
Looking ahead, more advanced conversational ad formats are expected: sponsored answers, embedded product recommendations, AI agent handoffs, and transactional prompts within dialogues. These context-aware, intent-driven experiences will redefine performance marketing, shifting the focus from click-based attribution to richer engagement metrics like interaction summaries and intent graphs that better reflect actual consumer behavior.
By 2029, spending on AI search ads in the US will reach $26 billion, according to eMarketer, which is approximately 14% of total search ad spending. Retailers will need to engage in proactive, flexible budget allocations to enable rapid experimentation with these formats. This in turn will allow retailers to capture real-time insights and quickly refine tactics to maximize returns. Early participation in pilot programs from leading AI providers can further reveal consumer engagement trends and effective strategies. This proactive stance helps executives not only understand but also influence the nascent AI-driven advertising landscape.
By 2029, spending on AI search ads in the US will reach $26 billion, according to eMarketer, which is approximately 14% of total search ad spending. Retailers will need to engage in proactive, flexible budget allocations to enable rapid experimentation with these formats.
2. Building Retailer-Owned Agentic Experiences
Retailers can differentiate by developing three types of proprietary AI agents that offer experiences third-party agents cannot replicate.
Brand Agents. Retailers can gain a significant competitive edge by deploying specialized AI-powered brand agents that reflect their unique identity and customer insights. Whereas third-party agents offer largely uniform and broad-based experiences, brand agents utilize deep domain expertise, proprietary data, and customized interactions to provide a higher level of personalization that third-party agents cannot replicate. (See “Brand Agents Offer Highly Personalized Support.”)
Brand Agents Offer Highly Personalized Support
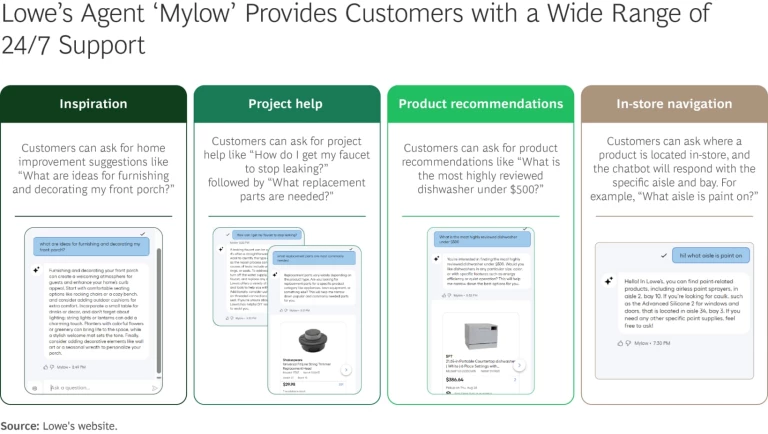
- Lowe’s has introduced Mylow, a specialized AI agent offering personalized home improvement guidance focused on do-it-yourself (DIY) customers. Customers can ask targeted questions, from project inspiration and detailed advice to locating specific items in-store. (See the exhibit.) MyLow leverages the company’s proprietary knowledge of products, layouts, and DIY methodologies.
- Instacart integrates a personalized AI assistant into its search interface. The AI agent interprets user prompts to suggest relevant products and recipes and build shopping carts, directly from users’ natural language queries. By embedding this AI within the existing search framework, Instacart simplifies the purchasing journey.
Workforce Agents. AI-driven workforce agents are transforming employee productivity and customer service capabilities, enabling in-store associates to respond swiftly and effectively to customer inquiries and operational challenges.
AI agents are also improving the efficiency and effectiveness of retail e-commerce operations across a wide range of use cases. In customer acquisition, AI shortens creative cycles from weeks to hours by generating and scaling ads, social content, and blog posts. On-site, AI enhances the customer experience through supercharged personalization and enriched product pages featuring detailed information, improved visuals, and concise review summaries. Behind the scenes, AI streamlines product data management to ensure consistency, accuracy, and faster time-to-market. In parallel, it monitors business performance by automating reporting and rapidly surfacing insights, allowing teams to adjust strategy quickly.
Emerging solutions illustrate the potential: Trustana provides an AI-driven suite for e-commerce performance, supporting product data management, enriched descriptions, and optimized content taxonomies for natural-language processing. Pencil, another tool, is an AI-powered ad maker that enables brands to effortlessly create and scale high-quality, realistic photo and video content.
Partner Agents. Partner agents automate and enhance interactions with merchants and suppliers, significantly improving efficiency. For example, Mirakl’s Connect platform enables sellers and brands to seamlessly onboard their catalogs, link with the right marketplaces, and leverage AI tools to advertise, cut costs, save time, and drive growth. In addition, Mirakl has introduced Nexus, which allows all merchants (retailers, sellers, suppliers, and brands) to connect to agentic platforms. This enables autonomous discovery, transactions, and post-sales management. (See “A Platform Provider’s Perspective.”) As another example, Walmart plans to launch an AI-driven agent, named Marty, to streamline vendor onboarding, optimize order management, and facilitate advertising campaigns.
A Platform Provider’s Perspective
“We're on the cusp of the next major commerce shift, after web commerce and platform models prevailed. Agentic commerce won't be another channel to manage, but rather a fundamental shift toward high-context, conversational discovery.
“Merchants will need to decide whether they partner with AI platforms in order to optimize what, where, and how to sell, in addition to optimizing their owned agents. Success will derive from an 'agent-ready' commerce design, including impeccable product data, competitive pricing, accurate stock availability, and seamless after-sales support.”
3. Building Agentic Foundations
Retailers need a robust foundation that supports scalable AI integration and facilitates secure, seamless operations.
AI and Data Platforms. Retailers should develop a sophisticated and scalable data infrastructure capable of robust AI integration. Central to this effort is adhering to the Model Context Protocol (MCP), an emerging standard that streamlines interactions between AI agents and back-end systems. MCP functions much like a universal adaptor, simplifying integrations across diverse AI platforms and reducing the complexity and resource intensity of scaling AI capabilities. By adopting MCP, retailers can facilitate secure interoperability among varied AI applications and services.
Measurement and Visibility Tracking. Retailers can leverage advanced analytics tools designed explicitly to track and assess brand visibility and performance across GenAI platforms. These tools allow companies to regularly monitor and analyze critical metrics, including AI-generated brand mentions, citations, and visibility rankings. Retailers gain actionable insights by understanding the nuances in how different AI models reference and prioritize brands.
Operating Model and Governance. A comprehensive AI governance framework encompasses responsible AI practices, clear roles and responsibilities, robust risk management, and effective use-case lifecycle management. Such frameworks ensure ethical considerations and regulatory compliance are integrated into daily AI operations.
Talent and Skills Development. In an AI-first organizational culture, humans strategically set the vision while AI agents effectively execute tasks. Retailers need to redefine roles and responsibilities, shifting from traditional human-driven processes to dynamic agent-driven workflows. This organizational transformation involves continuous investment in training and development to equip teams with AI competencies, including strategic oversight, decision-making capabilities, and technical expertise.
The Next Frontier: Agent-to-Agent Commerce
Agentic commerce is rapidly advancing toward full autonomy. Today, AI agents primarily assist consumers by surfacing personalized recommendations and simplifying product comparisons. But as trust in these systems grows, agents will increasingly handle end-to-end transactions—navigating product discovery, decision making, and checkout entirely within conversational interfaces, with little to no interaction with retailer websites.
This evolution sets the stage for a new frontier: agent-to-agent commerce. In this model, third-party agents will shop on behalf of consumers by leveraging their own capabilities and working directly with brand agents to finalize purchases. These interactions will continually optimize for consumer preferences, requiring little to no human input.
For retailers, success will hinge on reorienting their platforms so they are easily discoverable by third-party agents, launching their own agents that preserve brand value in automated interactions, and ensuring their agents can seamlessly connect, communicate, and operate in the broader ecosystem.
AI agents aren’t just another wave of digital innovation—they are fundamentally reshaping the retail landscape. While almost all global retailers are exploring agentic commerce, they are not moving fast enough. Those who move now by investing in agentic capabilities and building AI-native experiences will define the next era of customer engagement, brand relevance, and operational efficiency. Those who wait risk becoming invisible, disintermediated from the customers they once knew. The window to lead is rapidly closing, but for those bold enough to act, the upside is transformative.






