Despite successive technological revolutions—from the internet boom to generative AI—productivity growth remains disappointingly sluggish. Consider the European Union, where GDP per hour worked has risen by just 0.6% annually in recent decades. This lackluster growth contradicts the widely held expectation that advanced technologies would rapidly boost efficiency and replace human tasks at scale.
The reality is strikingly different: technology's potential to dramatically improve productivity remains largely untapped. Recent BCG research underscores that the GenAI revolution, at least so far, is no exception to this productivity paradox. Among more than 1,000 companies studied, only 4% have developed cutting-edge AI and GenAI capabilities across functions and are using them to consistently generate substantial value.
Organizations face two main barriers to translating technological advancements into substantial productivity gains. First, many companies implement advanced technology within outdated workflows rather than rethinking those processes entirely. Simply put, new technologies demand new, disruptive ways of working; applying innovative tools to old methods severely limits their potential. Second, fragmented governance and departmental silos cause narrow priorities to override broader organizational objectives, amplifying inefficiencies and eroding margins.
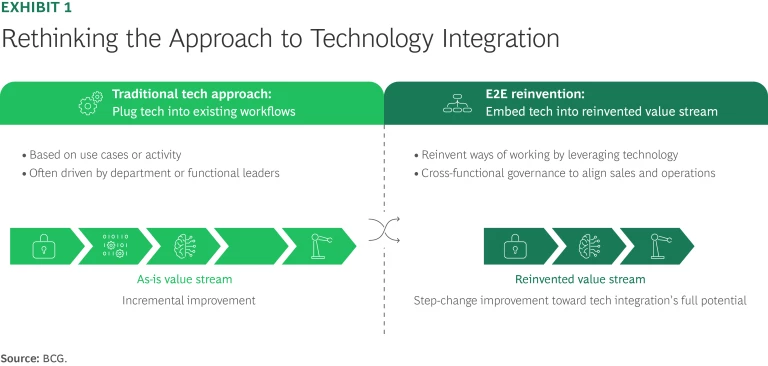
To overcome these barriers, organizations must embrace an end-to-end (E2E) reinvention strategy, fundamentally transforming ways of working and breaking down organizational and knowledge-related silos. Rather than optimizing isolated tasks, this approach rethinks entire workflows—eliminating frictions and inefficiencies, focusing on unmet needs, and seamlessly driving processes across different departments, such as sales and operations. (See Exhibit 1.) Companies can unlock breakthrough productivity gains, promote significant cost efficiencies, and open new avenues for value creation, typically achieving three to four times the impact of traditional incremental improvements.
Stay ahead with BCG insights on operations
Eliminating the Barriers to Productivity Gains
The primary motivations for introducing new technology are to enhance efficiency, improve operational capabilities, and gain a competitive advantage. Specifically, technology can streamline processes, automate tasks, and facilitate communication, leading to cost savings and increased productivity. Furthermore, embracing technological advancements can help businesses stay ahead of competitors in a rapidly evolving market.
E2E reinvention allows organizations to capture these benefits by streamlining processes through more effective technology implementation and by aligning cross-functional teams to drive cohesive strategic execution. The key is to regard technology not as a problem solver but as an accelerator of change. Real productivity gains come from stepping back to rethink processes from end to end and address the frictions and needs that truly drive impact.
Rethinking Processes Before Applying New Technology
Many organizations attempt to accelerate technology adoption by simply layering new systems onto existing workflows, but optimization requires first reimagining those workflows end to end. CIOs, often lacking explicit accountability for business outcomes and business process improvements, tend to reduce risks by deploying technology within the current operational framework rather than using implementation as a catalyst for meaningful transformation. This incremental approach yields modest efficiency gains at best and often leads to the automation of existing inefficiencies.
In contrast, E2E reinvention comprehensively rethinks and optimizes workflows with the specific objective of integrating new technology. This holistic approach generates far greater, synergistic impact because the technology becomes deeply embedded into fundamentally redesigned processes from the outset. Examples of the applications that can benefit from this integrated approach include customer relationship management, enterprise resource planning, and GenAI implementation.
CRM. Rather than merely digitizing current commercial processes, companies can leverage CRM deployments as opportunities to reimagine entire customer journeys. This could involve reconsidering pricing strategies, simplifying credit policies, or standardizing contract management. When organizations introduce a new CRM system alongside such updates, the technology becomes a powerful driver of behavioral change. This approach creates a valuable synergy: clearly defined policies ease CRM implementation, and simultaneously, the new CRM platform accelerates the adoption of these new practices across the organization.
ERP. ERP systems have the most impact when deployed within fully reengineered and simplified workflows. Instead of automating existing steps, companies can use ERP systems to, for example, introduce advanced sales and operations planning, create integrated and transparent supply chains, or radically streamline procure-to-pay processes. Another advantage of simplifying processes upfront is substantially lower implementation costs. By minimizing complexity, companies can save on deployment expenses and position the ERP system as a lever for operational excellence, dramatically improving quality and productivity.
GenAI. Today, most companies are experimenting with siloed GenAI use cases that optimize existing workflows incrementally rather than reimagining service delivery or ways of working. Employees primarily use GenAI as a thought partner to solve standalone problems. For example, in a recent project aimed at boosting HR productivity, user interviews showed a clear preference for GenAI tools that merely sped up the drafting of job descriptions—tasks traditionally done manually. However, a more ambitious, holistic approach to leveraging GenAI could fundamentally reimagine workforce planning. For instance, AI could strategically map organizational goals to the skills and capabilities required, transforming workforce management and strategic hiring.
Unifying Governance and Strategy
Siloed governance and fragmented strategies remain significant obstacles to productivity gains, particularly in organizations where sales and operations departments act somewhat independently. In many companies, sales teams often operate without real-time access to stock availability or customer payment status, leading to inefficiencies and financial losses.
Many companies do not realize how frequently their sales orders result in negative margins. For example, a consumer firm that used value stream mapping discovered that 20% of its orders were unprofitable; sales representatives often granted concessions, such as expedited deliveries or additional credit, without fully considering their cost implications. These practices are particularly problematic given that, in both service-based and manufacturing companies, order-to-cash expenses can constitute a significant portion of variable costs, although they are often characterized as fixed costs. When sales teams overlook these costs in pricing decisions, negative-margin transactions are almost inevitable.
Poor cross-functional alignment often creates a paradox: companies deliver what they have not sold or sell what they cannot deliver. An engineering firm illustrates these challenges. During the quotation phase, the firm’s designers invested significant effort in providing detailed consulting, believing this service differentiated them from competitors. However, because the sales team did not properly account for the added value when bidding for the project, the firm inadvertently ended up competing primarily on cost rather than expertise. At the same firm, sales teams frequently committed to overly ambitious project timelines, leading to costly contract penalties and reputational damage when operations teams failed to deliver.
Cross-functional collaboration is also crucial for fully realizing the benefits of technology-driven improvements, as investments by one department frequently generate value in another. For instance, when the sales team implements a new CRM system, the enriched user data collected empowers the growth teams to perform more insightful pricing analyses. The same data will help the operations teams to optimize costs. Similarly, paid advertising teams can utilize this customer information to create highly targeted ads that resonate more effectively. To maximize these cross-functional benefits, teams should collaborate during the planning and implementation stages of new-technology deployments, ensuring that the systems capture and deliver the most valuable information across the organization’s departments.
End-to-end value stream analysis helps organizations identify critical bottlenecks and unmet needs. Cross-functional collaboration then ensures that resources are directed toward the high-impact areas, rather than allowing each function to independently address its isolated issues. When teams collectively focus on optimizing bottleneck steps, they can achieve significant improvements in overall process performance. In contrast, efforts invested in optimizing idle or already efficient steps typically result in minimal gains.
Five Ways to Capture the Benefits
E2E reinvention requires that companies take five concrete actions.
1. Reimagine value creation. Emerging technologies enable new possibilities, but many organizations limit themselves to incremental improvements in existing products, services, or pricing and delivery strategies. Instead, technological advances should serve as a catalyst for the fundamental rethinking of offerings while strategically aligning them with operational strengths. One powerful method to drive transformative thinking is to consider provocative "what if" scenarios, such as: What if a major tech company entered our market? What if we had to achieve a tenfold increase in performance? What if GenAI becomes the invisible force behind our biggest business decisions? Considering these questions pushes teams beyond the limits of conventional thinking and encourages breakthroughs in innovation and value creation. For example, a "thinking in new boxes" exercise enabled a traditional broadcaster to identify innovative opportunities, such as linking viewers’ program selections to smart-home-lighting automation, as well as offering hypercustomized content and targeted advertising.
To ensure that transformative potential translates into measurable outcomes, organizations should set bold aspirations for return on technology investment (ROTI). A fundamental benchmark is a 10x ROTI—achieving $10 million in impact for every $1 million spent. Setting disruptive targets not only fosters accountability but also encourages creativity and bold strategic thinking. Without ambitious goals, companies risk achieving only modest gains rather than the step-change efficiencies needed for genuine transformation.
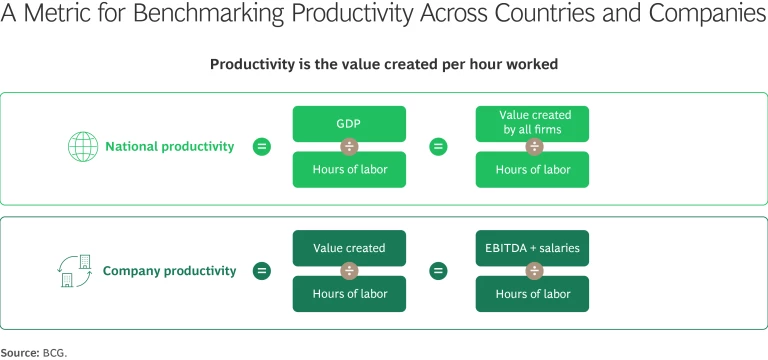
Crucially, organizations must maintain clear visibility into ROTI across every stage of technology implementation, verifying that each deployment phase contributes directly to measurable value creation. To evaluate the impact of technology on productivity, a company can measure the value created per hour of labor across its organization. (See “A Smarter Way to Measure Company Productivity.")
A Smarter Way to Measure Company Productivity
Instead, companies should connect E2E technology investments and workflow improvements directly to a comprehensive productivity metric. The most effective way to achieve this clarity is to measure productivity as "value created per hour of labor," defined as the sum of EBITDA and employee salaries divided by total hours worked. This metric captures how much value a company generates for every hour of human effort expended. In so doing, it translates a national productivity metric—GDP per hour worked, where GDP is the total value created by all enterprises within a country—into a company-level equivalent. (See the exhibit.)
2. Eliminate legacy activities. To avoid merely digitizing existing processes, companies need to map value streams and remove outdated practices. (See “Value Stream Mapping Is Essential for E2E Reinvention.”) Our analyses frequently show that 20% to 30% of activities are legacy tasks that were once essential but have lost their relevance. For example, organizations may continue entering data into systems for metrics that are no longer utilized, maintain outdated control checks despite significantly improved failure rates, or rely on obsolete methods even though more efficient technologies are available.
Value Stream Mapping Is Essential for E2E Reinvention
By tracing the amount of labor time spent on each process step and linking it to specific outputs, VSM allows companies to quantify labor cost per unit, such as per order. This often reveals that some orders are structurally unprofitable. VSM also identifies bottlenecks, idle periods, redundancies, and inefficient behaviors—exposing hidden improvement opportunities. VSM is especially powerful in service-oriented processes, where flow is not tied to physical materials and is therefore less visible.
3. Enable cross-functional alignment. True reinvention requires dismantling organizational silos and enabling cross-functional alignment to effectively drive strategic execution. Financial objectives should cascade down to specific operational goals and performance metrics that are monitored and steered by each manager in the organization. This structured approach, often visualized in a KPI tree, ensures that every employee’s performance metrics are directly tied to overarching business outcomes such as EBITDA or cash flow. By linking individuals’ goals and objectives to the company’s financial targets, unified governance enhances accountability, streamlines coordination across departments, and ensures that productivity gains are realized across the entire organization.
4. Address the root causes of inefficiencies. Many downstream inefficiencies originate from overlooked issues upstream. In order-to-cash processes, for example, invoice errors or late payments often arise from poorly structured orders or excessive, nonvalue-adding customization. Identifying and resolving these root causes are crucial for maximizing productivity. By targeting inefficiencies at their source, organizations can achieve substantial, sustainable impact rather than localized, temporary enhancements.
5. Promote a “sales to cost” strategy. Sales teams must shift from purely volume-driven objectives to approaches that promote cost efficiency, seamless customer journeys, and profitability. Often, sales representatives lack real-time visibility into inventory status, order-to-cash expenses, and the true financial implications of commercial concessions, leading to margin erosion. Each pricing decision—such as extending payment terms, agreeing to rush deliveries, or offering discounts—carries direct costs related to labor and operational complexity.
Making these hidden costs transparent to sales teams and embedding them into incentive structures empowers representatives to steer customer choices. A sales-to-cost strategy encourages sales personnel to guide customers toward decisions about payment methods, delivery schedules, and product selections that enhance efficiency and profitability and streamline operations and customer journeys.
E2E Reinvention in Action: GenAI-Powered Workflows
A leading European media company demonstrated the transformative impact of the E2E approach. The company had begun experimenting with more than 100 siloed AI use cases across departments, including marketing, finance, and procurement. These pilots aimed to generate incremental improvements within existing workflows, but they failed to deliver meaningful P&L impact: fragmented tools, disconnected processes, and a lack of strategic coordination had diluted GenAI’s transformative potential.
BCG worked with the company to break out of this pattern by reimagining E2E workflows using GenAI. We began by applying a structured four-lens evaluation framework—desirability, feasibility, viability, and impact—to identify disruptive, high-value opportunities across the business. This approach ensured a sharp focus on opportunities that addressed clear user pain points, aligned with strategic priorities, were scalable with existing capabilities, and could drive tangible business value.
Marketing quickly emerged as a high-impact domain. It faced a familiar set of pain points: high third-party and FTE spend, fragmented content production processes, and difficulty staying ahead of market trends. GenAI’s ability to generate high-quality content quickly made it a natural fit—but only when applied through a fully reimagined operating model.
At the heart of this transformation was BCG’s content amplifier: an E2E marketing agent that combines best-in-class GenAI capabilities with third-party and proprietary client insights to generate on-brand content at scale.
This E2E approach delivered substantial impact:
- €4 million in savings in the first year, with total projected savings of €11 million by 2027
- More than 80,000 hours of manual work eliminated through automation
- Accelerated content production, enabling faster go-to-market execution across channels
Beyond efficiency gains, the content amplifier also enhanced effectiveness. By producing highly relevant, insight-driven content at scale, the company saw significant uplifts in campaign engagement. This echoed similar results observed in other BCG engagements, such as a global spirits company that cut its spending on external digital-marketing services by 80% while increasing ad engagement by up to 60%.
Crucially, this transformation was underpinned by a robust governance and operating model. An AI transformation cockpit was implemented to track KPIs, ensure accountability, and uphold responsible AI standards. High-impact GenAI initiatives were prioritized and funded at the C-suite level, with governance owners focused on driving tangible P&L outcomes.
In short, E2E reinvention, powered by GenAI and supported by a new operating model, enabled the company to break free from legacy constraints and unlock both efficiency and effectiveness in equal measure.
The Roadmap for E2E Reinvention
Successful E2E reinvention requires a phased roadmap that systematically guides organizations from initial assessment through full-scale implementation. (See Exhibit 2.)
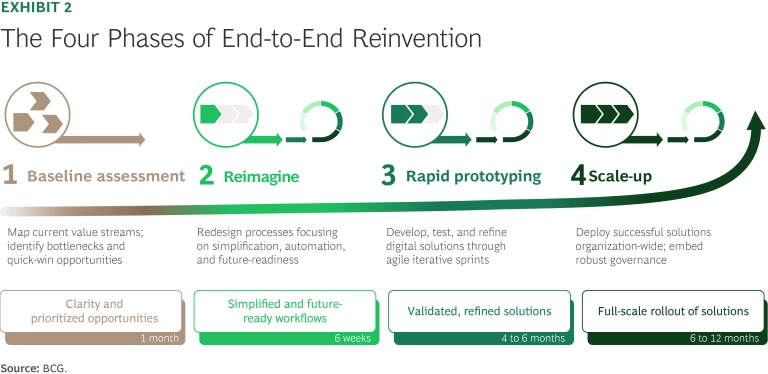
By providing clearly defined stages, actionable milestones, and strong governance support, the E2E roadmap ensures that transformation becomes deeply embedded within the organization’s operational culture.
As technological disruption accelerates, continuous reinvention is essential. By adopting E2E reinvention, organizations can unlock technology’s full potential—achieving substantial cost savings through simplified processes and reduced complexity in implementation. Equally important, E2E reinvention drives a fundamental shift toward customer-centric innovation. In a business environment where agility and responsiveness define success, organizations that commit to E2E reinvention position themselves for sustained competitive advantage. Now is the time to rethink, reimagine, and reinvent.






