GenAI’s uses, its limitations, and its meaning for the creative process have dominated marketing conversations since the technology entered the mainstream in 2022. Big announcements touting new tools’ stellar video and image prowess fueled the hype, but those same tools continue to exhibit growing pains, including glitches, crashes, and hallucinations.
The perceived gap between hype and performance may explain why deployment of GenAI tools in creative development remains limited at the enterprise level. For many companies, GenAI is still at an experimentation stage, even though marketing budgets are getting squeezed and cost control and efficiency are on the CMO’s mind more than ever.
At the same time, however, tool capabilities seem to be converging at a higher level of quality, and the performance gap between leading platforms is narrowing. To understand what is preventing companies from deploying GenAI more widely in operational creative tasks, we looked at the technological and operational challenges that marketers face. To test the technology, we conducted a comparison across common creative GenAI tools that involved prompting them to create new campaign collateral instead of reworking or enhancing existing creative. The objective of this creative test was to assess the solutions’ technical capabilities and their capacity to enhance creative effectiveness.
We also surveyed 251 global marketing leaders, asking them how extensively they and their teams are adopting GenAI solutions and what expectations they have for the future. We concluded that as tool performance and public optimism continue to improve, the next phase of GenAI adoption will focus on operational readiness and implementation of the right adoption strategy by upskilling people, reimagining creative workflows, and selecting appropriate best-in-breed tools.
Stay ahead with BCG insights on marketing and sales
The Gap Between Optimism and Action Persists
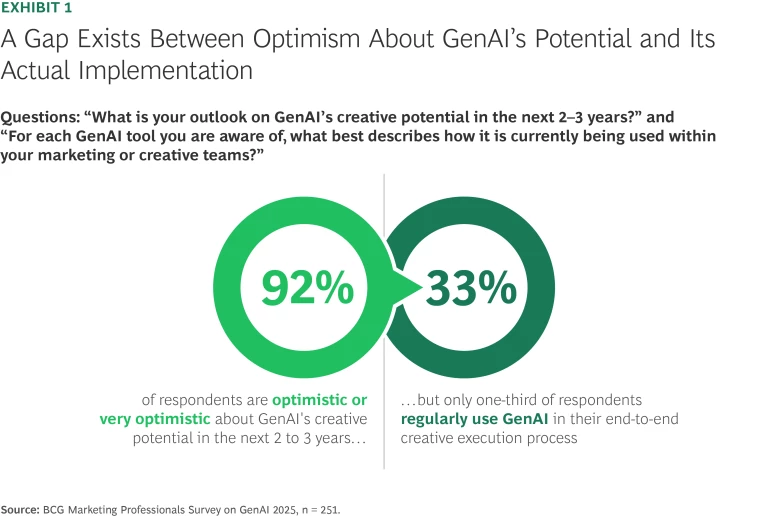
Insights from the survey highlight the gap between optimism about GenAI’s potential and actual implementation. Consistent with our findings from previous GenAI surveys, marketers remain excited and optimistic about GenAI’s potential. A stunning 92% of respondents were optimistic or very optimistic (versus cautious or skeptical) about GenAI’s creative potential over the next two to three years. Despite their optimism, however, those respondents are still mostly testing and experimenting. Only a third of respondents report end-to-end or regular GenAI usage, while two-thirds use the technology selectively or not at all. (See Exhibit 1.)
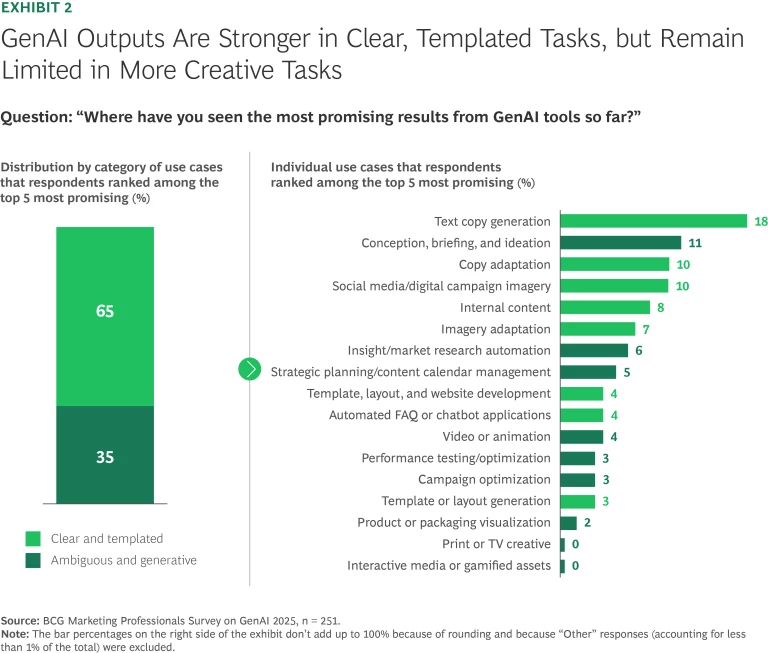
Of the use cases that marketers in our survey ranked as most promising, two-thirds centered on structured and templated content types such as copywriting and editing, social media, and internal content. Less than 5% of respondents gave a high ranking to any more elaborate use case, such as video or animation generation, print or TV creative, or product or packaging visualization. (See Exhibit 2.) This hesitation may stem from lingering technical issues that have prevented brands from fully trusting GenAI for creative production.
To test this hypothesis, we gave leading and emerging GenAI tools illustrative prompts to generate images for fictitious marketing campaigns. In the first example, we asked the tools to show a cozy work desk with a laptop, coffee cup, and notebook, in line with the kind of creative that a furniture or home goods retailer might use. In the second example, we tested the impact of prompt quality by asking the tools to generate collateral for a coffeeshop and for a sneaker brand.
Historically, we have seen large variations in creative quality, but our tests showed that tool capabilities have largely converged, leaving a narrower performance gap between platforms.
In our experiment, creative output was surprisingly strong under ideal conditions, such as well-structured prompts and clearly defined goals. Brief, vague, and unspecific prompts, however, yielded poor—or at best generic—output. Creative quality thus depends heavily on user input. Prompting skills, iteration, and familiarity with the tools significantly impact results. (See Exhibit 3.)

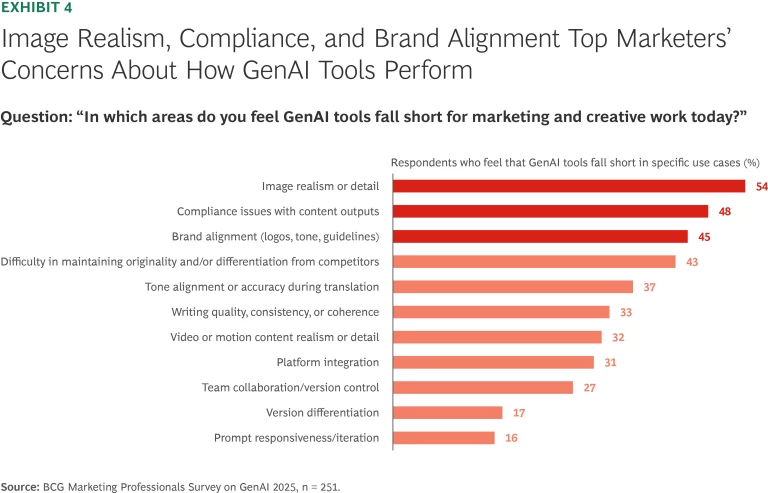
Our survey corroborates these findings. One-third of respondents see limited team fluency and prompting skills as a key barrier to broader GenAI adoption. Even so, marketers seem to see creative output as only loosely connected to prompting skills and user input. When asked about the biggest shortcomings of GenAI, they emphasized quality-related issues such as image realism and detail, brand alignment, maintaining originality and differentiation from competitors, and writing quality. Only 16% named human input factors as a key concern, even though the two are inherently connected. (See Exhibit 4).
We see two potential ways to address this gap between quality and human input. First, a wide range of GenAI deployment models are available, with the hybrid approach of building in-house capabilities with select partnerships and off-the-shelf solutions remaining the most popular. Continuing to build dedicated in-house models and capabilities will be crucial for successful use of GenAI. Second, improving employee training and investing in better prompting can dramatically increase the quality of creative output. Survey respondents already recognize talent upskilling, increased training time, and updated workflows as key accelerators for their creative work.
Reinventing Creative Workflows
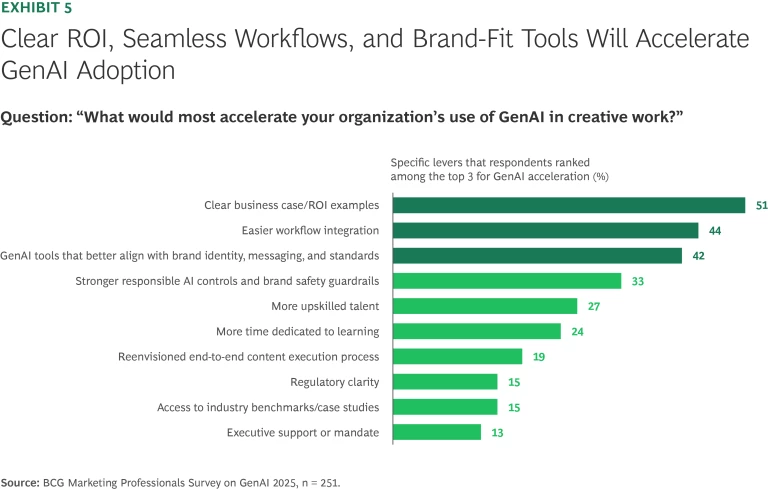
Another discrepancy that our survey revealed involves how marketers think about creative workflows. When we asked what would most accelerate their organization’s use of AI, 44% of respondents said easier workflow integration, while only 19% cited an end-to-end reinvention of the content execution process. (See Exhibit 5.) This is an important distinction. GenAI can certainly augment existing processes, but leading players are using it to transform how they operate. BCG recently helped an education company shift to a GenAI-first model, resulting in a 30% to 40% reduction in FTE hours for content production while maintaining internal quality standards. The key to unlocking these efficiency gains was not to integrate AI into existing processes, but to redesign the processes to let the technology shine.
Content quality is also a function of the tools that marketers choose to perform certain jobs. Our research found that awareness and usage are highest for GenAI solutions from large, well-known tech companies. Although their underlying large language models (LLMs) are the backbone of many GenAI applications, they are most suitable for generalist tasks. Meanwhile, a wide range of specialized tools target not only relatively narrow marketing use cases such as copywriting or image generation, but also highly specific use cases such as generating images for retail product detail pages.
The output quality for these niche tools may not yet be up to some marketers’ standards, but using GenAI tools for creative reinvention doesn’t have to be an either-or proposition. Production is only one aspect of the creative process, and many available tools can support other processes, such as workflow and research. Incorporating these tools into workflows can unlock efficiencies to allow marketers to invest more time in high-value tasks that improve output quality. Yet our research shows that these niche tools currently suffer from low awareness and usage.
How Brands Can Broaden GenAI Adoption
GenAI has made remarkable leaps in a short time. But despite the technology’s massive potential, it is not yet a plug-and-play option for creative reinvention. To reach their full potential, GenAI deployments must focus on several key success factors. (See Exhibit 6.)
Upskilling People. GenAI tools can deliver high-quality output under ideal conditions, but they may yield subpar output in response to poor prompting. Creating ideal conditions depends on human input: well-structured prompts, targeted iterations, and clear goals. To create these conditions within their teams, companies should continuously upskill and train employees. Advanced companies today go one step further, using LLMs to create prompts, which they then feed into specialized tools. Knowing how to get the most out of these new tools is important for quality and for adoption. The learning curve for these technologies can be challenging, even for experienced creatives. It requires a shift in mindset from output generator to creative co-pilot.
Reinventing Operational Workflows. Many companies experiment with GenAI in isolation or try to “lift and shift” part of their existing workflow to GenAI. But GenAI tools shine brightest when integrated and embedded in workflows that are optimized for the technology. In terms of BCG’s Deploy-Reshape-Invent framework, many companies are still firmly in the deploy stage. It is time for companies to reimagine critical creative workflows, including how employees work within marketing.
Shifting to Best-of-Breed Tools. Most survey respondents employ one or two general-purpose GenAI models. But new targeted solutions for specific use cases in the workflow—from research and ideation to workflow management and creative execution across text, image, and video—are emerging every day. Deploying GenAI goes beyond image or text generation. BCG recently supported a global consumer packaged goods company in developing a GenAI-enabled strategic briefing tool that allows marketers to develop high-quality briefs, resulting in improved velocity and campaign effectiveness. Companies should continue testing such solutions, find the best tools for their needs, and coordinate their workflows across these tools to unlock efficiency and allow their teams to focus on high-value, strategic tasks.
GenAI offers vast potential for marketers to reinvent creative processes, but companies remain hesitant to adopt the technology at scale because they perceive the generated content as lacking in quality, authenticity, and brand image fit. However, the technological foundation of GenAI has improved dramatically, and tools can now deliver high-quality output under ideal conditions. And crucially, using GenAI in creative workflows is not an either-or question. Brands have a wide range of tools available to simplify, augment, and transform existing workflows beyond creative production.






