Partnerships have quietly become powerful engines of strategic growth. Once seen as secondary to traditional M&A, joint ventures and strategic alliances (JV&A) are now taking on a more central role in corporate strategy. As M&A volumes have generally declined over the past eight years, JV&A deals have proven more resilient—offering the adaptability needed in fast-changing markets.
Today’s JV&A landscape is broader and more dynamic than ever. These partnerships provide companies with flexibility, regional access, and sector-specific agility—critical advantages amid ongoing geopolitical uncertainty. Executives increasingly see them as accelerators of innovation, means of entry into new markets, and stabilizers of core operations.
This evolution has repositioned JV&As as key levers for sustainable growth and long-term resilience. A close look at performance data reveals both their rising strategic relevance and the importance of experience: companies that learn to effectively execute these transactions are best positioned to unlock their full potential.
Stay ahead with BCG insights on digital, technology, and data
JV&As Are Evolving
M&A activity has trended downward since 2017, aside from a short-lived boost due to opportunistic buying at depressed prices as the COVID-19 pandemic subsided. Yet JV&A deal volumes have stayed strong following a post-pandemic reset in US, Chinese, and cross-border deals. (See Exhibit 1.)
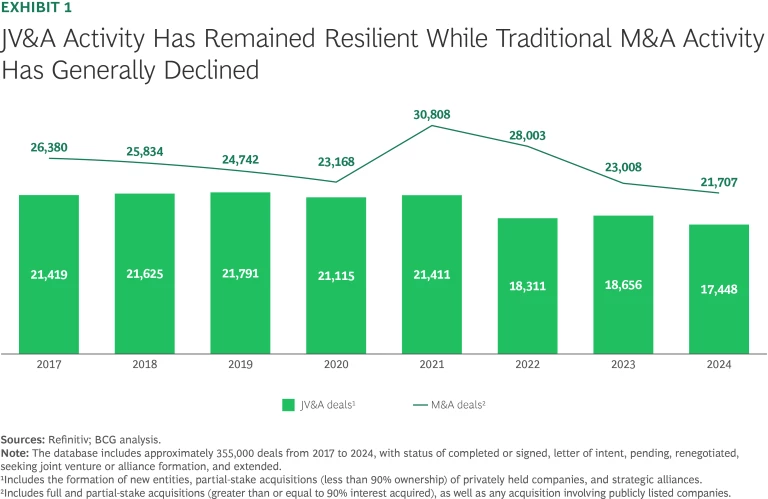
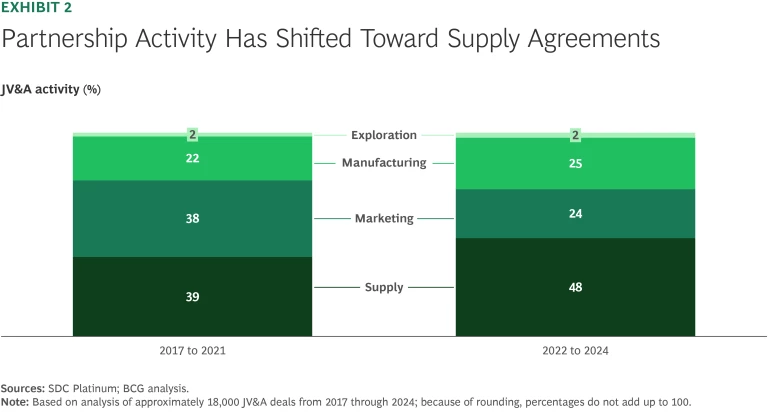
This resilience underscores a fundamental shift: companies increasingly recognize the strategic flexibility and competitive advantages associated with JV&A compared with traditional M&A. Historically, JV&As primarily entailed marketing and manufacturing partnerships designed to boost production capacity and distribution reach. In recent years, a growing number of partnerships have focused on supply chain resilience and risk mitigation. (See Exhibit 2.) The trend has accelerated since 2020, especially in the retail and health care sectors, where companies are partnering to secure inputs and ensure operational continuity. These alliances can reduce exposure to global shocks, mitigate risks, and allow for the sharing of costs.
An example is the alliance between immuno-oncology company Imugene and global biopharma leaders Pfizer and Merck KGaA. To improve the likelihood of clinical and commercial success, Imugene partnered with these major players to access Avelumab, an advanced immunotherapy, for use in trials of its novel gastric cancer treatment, HER-Vaxx. The deal enabled the companies to explore new treatments that address a significant unmet need, thereby increasing their potential impact in the market.
Investor Confidence Is Increasing
Market reactions reinforce the strategic importance of these partnerships. Investor confidence in JV&As has grown notably, as evidenced by the immediate positive market responses following partnership announcements. BCG’s analysis has found that more than half of JV&A announcements lead to positive cumulative abnormal returns (CAR), reflecting strong investor approval and optimism.
At the same time, investors’ perceptions of JV&As relative to traditional M&A are improving. For example, in the past, M&A deals had higher CAR around the time of the deal announcement. However, as shown in Exhibit 3, JVs have recently generated stronger positive reactions. This shift signifies the growing market perception that partnerships such as JVs are not just a viable alternative to M&A but are often a strategically superior choice.
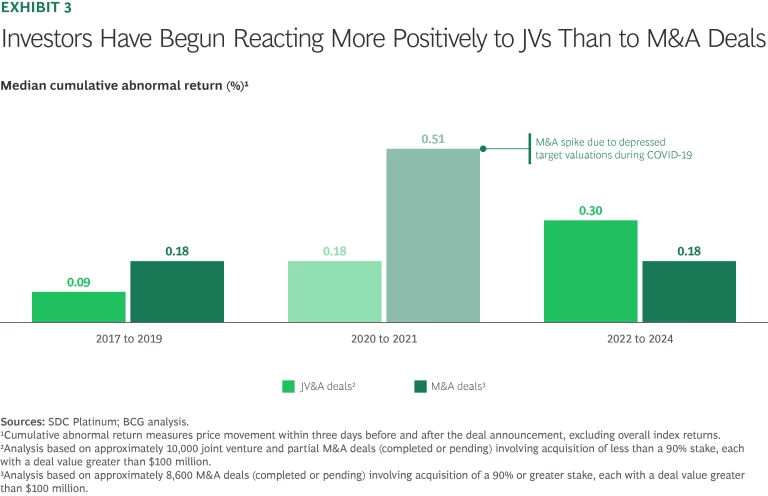
That said, the short-term investor confidence in partnerships varies by industry. JVs’ overperformance in CAR relative to M&A is more apparent in the telecommunications, consumer, industrials, and utilities sectors.
The Long-Term Edge: Experience Matters
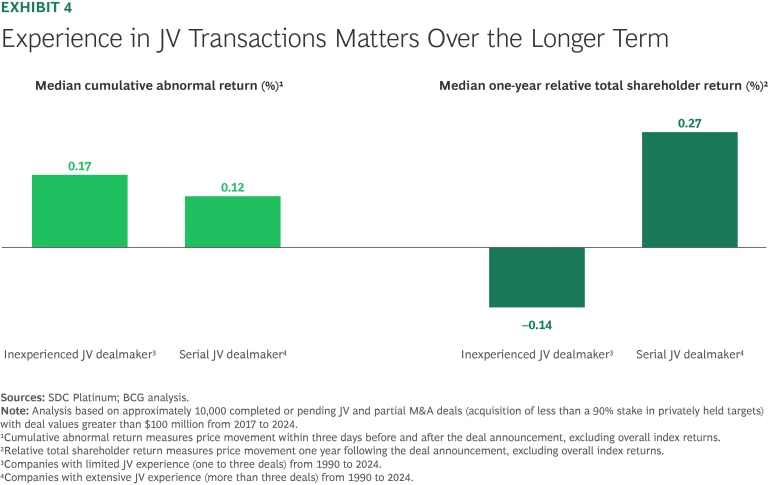
While immediate market reactions underscore investor confidence in JV&As, their long-term success and value creation largely hinge on experience and expertise. Companies with extensive experience executing JV&A transactions achieve superior results compared with their less experienced counterparts.
Our research indicates that the JVs executed by serial dealmakers significantly outperform those of first-time participants, with a median one-year relative total shareholder return (rTSR) approximately 0.4 percentage point higher. (See Exhibit 4.) This performance differential is even more pronounced for JVs involving the formation of new entities rather than strategic alliances.
Eli Lilly is a prime example of a serial JV&A dealmaker, having completed some 15 partnerships over the past five years. For instance, in 2021, the company partnered with Indian pharmaceutical player Cipla to enhance the reach of its diabetes treatments Humalog and Trulicity. Lilly transferred its rights to sell, promote, and distribute these products in India, while Cipla agreed to leverage its extensive commercial infrastructure to improve patient access. In the year following the partnership announcement, the parties generated an rTSR of 0.9%—more than double the average for serial JV&A dealmakers—underscoring how experience can translate directly into shareholder value.
The correlation between experience and superior returns aligns closely with findings from BCG’s previous M&A research on acquisitions: serial acquirers create superior returns, while less experienced acquirers tend to destroy value. Moreover, the value associated with JV&A experience has become more pronounced in recent years, highlighting the importance of internal capabilities and deal-making sophistication in driving sustainable shareholder returns. Many of the most successful serial JV&A dealmakers—including leading biopharma companies such as Merck, Lilly, and Pfizer, as well as oil and gas giants like TotalEnergies, Saudi Aramco, and BP—have built dedicated partnership or JV teams distinct from their M&A functions. This organizational separation reflects the recognition that JV&A execution requires specialized skills in structuring, governance, and long-term value management.
Strategic Implications for Executives
All of these findings underscore how JV&As have emerged as strategic instruments to unlock innovation, access new markets, and build resilience. But to gain the benefits, executives must fundamentally rethink how they utilize partnerships.
Exploit JV&A when M&A is constrained. In markets characterized by high uncertainty, regulatory hurdles, or significant integration risks, traditional M&A strategies may be challenging or even unfeasible. JV&A offers a faster, lower-risk alternative, recognized by the market in superior CAR relative to traditional M&A.
Utilize partnerships to achieve core priorities. Companies have recognized the role that JV&A can play in providing supply chain resilience amid growing geopolitical tensions and global disruptions. Executives should continuously identify strategic goals that can be achieved by using JV&A not only for growth, but also to protect core operations and ensure long-term business continuity.
Build and institutionalize partnership experience. Organizations that approach JV&A as repeatable strategic processes, rather than as one-off experiments, outperform their less experienced peers in terms of rTSR. Institutionalizing partnership capabilities ensures long-term performance advantages and positions companies to leverage the strategic value of JV&A transactions.
JV&As have quietly but fundamentally reshaped the strategic playbook for executives. Our analysis highlights their growing role in strengthening resilience and delivering near-term market impact—advantages that investors are rewarding. But the full value of these partnerships hinges on experience. Executives who proactively build robust partnership capabilities will not only navigate today’s complexities with agility but also position their organizations for sustained innovation, growth, and competitive advantage in the future.






