Ambitious Growth Demands a Future-Ready, Capable Workforce
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is on a rapid growth trajectory, driven by Vision 2030’s ambitious plans - Saudi Arabia’s strategic framework to reduce its reliance on oil, diversify its economy, and develop public service sectors. We see it reflected in all kinds of new public infrastructure, development of megaproject destinations, and the strategic expansion of targeted economic sectors. This multifaceted growth demands a strong, future-ready and capable workforce to sustain and propel it across multiple levels.
New sectors, such as tourism, hospitality and entertainment, are emerging as cornerstones of the Kingdom's economy, including through megaprojects such as Qiddiya, and The Red Sea Project. These industries require a skilled workforce equipped to deliver exceptional guest experiences and operational excellence. Success in these sectors demands professionals who can combine technical proficiency with superior service delivery, creating memorable experiences that meet rising consumer expectations and international standards.
Established sectors like transport and logistics are seeing a major strategic surge in infrastructure and mobility projects (e.g., Riyadh Metro, Riyadh Air, King Khalid Airport). Their scale and increasing complexity demand both a large and skilled workforce. These sectors require expertise ranging from advanced technical capabilities to project management skills, with professionals who can handle increasingly sophisticated systems while maintaining operational efficiency and safety standards.
Frontier topics like artificial intelligence (AI) and sustainability are gaining prominence, demanding specialized skills and qualifications to lead the Kingdom into the future. As emerging technologies transform the workplace, the focus is shifting toward a hybrid workforce model where humans and machines complement each other's strengths. This requires professionals who can not only leverage AI and automation but also excel in uniquely human capabilities like complex problem-solving, emotional intelligence, and creative thinking – skills that will be crucial for the Kingdom's digital transformation journey.
Private sector players, such as real estate development companies, are leading large-scale, multiuse developments that transform the urban landscape. These projects combine retail, residential, leisure, and commercial spaces, requiring diverse talent pools—from frontliners to corporate teams—to manage and operate them effectively. Success demands professionals who understand integrated development principles and can deliver excellence across multiple asset classes while managing complex stakeholder relationships.
And entire destinations are being shaped and reimagined to elevate the experience for residents and visitors. From planning to execution and ongoing operations, these developments need a highly skilled workforce to deliver seamless experiences throughout the customer journey. These mega-destinations require professionals who can think holistically about user experience while managing the intricate operational demands of large-scale, mixed-use environments.
As the Kingdom continues this unprecedented transformation, developing its future human capital base is a national priority. It will require the concerted effort of national and regional government stakeholders, private sector, and the training and education ecosystem.
For megaprojects, the stakes are particularly high. As these transformative developments transition from concept to operations, they demand a diverse pool of skilled talent across industries including entertainment, sports, hospitality, and healthcare (Exhibit 1). For example, Diriyah alone anticipates the need for over 180K additional jobs by 2030.

Stay ahead with BCG insights on people strategy
Meeting the Kingdom’s critical demand for human capital will be challenging due to:
- The limited availability of specialized talent – some of the necessary skills and roles may not yet exist locally or are in scarce supply.
- Fierce competition for talent – as multiple projects ramp-up in parallel, the competition for talent will intensify.
- Emerging sector challenges – new industries may struggle to attract talent due to unclear career pathways, perceived role status, or concerns about job sustainability.
However, failure to secure the right talent poses serious risks to the success of these projects and destinations, including operational delays, increased recruitment costs, and failure to meet Saudization goals. A comprehensive Human Capital Strategy is essential to align workforce supply with demand, ensuring sustainability of this rapid growth and the socio-economic impact of these transformative projects.
Common Pitfalls Undermining Workforce Readiness
Several critical oversights commonly undermine human capital strategies and project success. The first is underestimating the impact of human capital planning. Brand credibility, particularly in customer-facing industries like hospitality and entertainment, is especially vulnerable to these failures, yet organizations often overlook the broader socio-economic and operational consequences.
A second major pitfall is delayed workforce planning. Many organizations begin their human capital initiatives only months before a project's operational launch. This results in rushed, reactive solutions, such as isolated training sessions or emergency recruitment drives, that fail to attract the right people or give them adequate preparation. Furthermore, this ad-hoc approach fosters a reliance on short-term expatriate workforce and difficulty to localize expertise and create a sustainable pool of Saudi talent. Such short-term fixes cannot replace a thoughtful strategy, as they do not address the systemic issues behind talent shortages. This lack of long-term vision leads to a misaligned and unsustainable workforce, with serious operational and financial consequences.
Thirdly, many megaprojects look at the issue in a siloed, piecemeal approach, focusing on select functions such as strategy, levels such as N-1 or topics such as sustainability only. This approach may appear as more focused and concrete but it sacrifices the big picture for short term results, thus failing to capture synergies in recruitment, training and partnership setting.
Fourthly, insufficient collaboration between industry and education sectors creates significant challenges. Many organizations fail to establish meaningful partnerships with educational institutions, leading to a persistent gap between academic programs and actual industry needs. This disconnect means graduates often lack the specific skills and practical experience required for megaprojects, while training providers develop curricula without real-time input from the market. Early engagement with universities, vocational training centres, and technical institutes is crucial for developing relevant programs and creating sustainable talent pipelines. Organizations that neglect these partnerships find themselves constantly struggling to find work-ready talent, spending significant resources on retraining new hires rather than building coordinated pathways from education to employment.
Building the future workforce requires taking a long-term, strategic approach that ensures human capital initiatives align with broader organizational goals and evolving demands. In Saudi Arabia, aligning with megaprojects' goals and demands in the short-, medium-, and long-terms will be critical.
Building Human Capital and Shaping the Future Workforce
Building human capital and shaping the future workforce requires a comprehensive strategy that spans the entire human capital value chain. While the framework presented here is designed with megaprojects in mind, its principles are equally applicable at both national and organizational levels. The approach consists of five key phases:
- Anticipate: Long-term Talent Planning
Leaders should begin by understanding their workforce needs at a granular level, segmented by job family, asset, and year. A dynamic model that forecasts these needs and aligns them with project timelines is essential. Organizations must outline the number of employees, specific roles, required skills, and asset locations. Implementation of a flexible demand model that tracks talent needs over time is crucial, allowing adaptation to project progress and changes. Such tools become especially powerful if they are AI-powered, allowing them to anticipate demand with increasing speed, flexibility and accuracy. - Create or Attract: Sourcing Talent
There are two pathways to sourcing talent – creation and attraction. The megaproject can partner with training and education providers to create local talent through development and upskilling, ensuring they are job-ready when needed. Programs should be tailored to the specific skills and competencies required by the sector and specific project, as identified in phase 1. Alternatively, it can leverage existing talent, identifying where to find candidates and how to attract them through targeted campaigns and a compelling employer brand. - Recruit: Talent Acquisition
Leaders and HR professionals must adapt the talent acquisition process to the specific needs of megaprojects, including large numbers of employees coming onstream at the same time, and diverse skill requirements. Technology plays a crucial role in streamlining recruitment, ensuring scalability, and developing onboarding programs that smoothly integrate employees into the organization. - Develop: Strengthen and Future-proof the Human Capital Base
At both the megaproject and national levels, strengthening and future-proofing the human capital base is of utmost importance. Organizations must provide employees with a continuous learning and development journey that anticipates tomorrow's needs while supporting their career progression. This means embedding lifelong upskilling opportunities that keep pace with evolving industry demands, establishing clear career pathways that adapt to changing roles, and ensuring technology-ready skillsets that prepare workers for increasing digitalization. Comprehensive leadership development programs are equally crucial to nurture future leaders who can navigate emerging challenges and opportunities. - Engage: Ensuring Employee Retention
As mentioned earlier, megaprojects should expect fierce competition for their talent. To retain their hard-won human capital, they must foster a strong organizational culture and loyalty through a holistic Employer Value Proposition (EVP). Such an EVP will typically include engaging initiatives that enhance job satisfaction and motivation, alignment with organizational values and long-term goals, and a workplace that encourages collaboration, innovation, and purpose.
Cross-Departmental Integration
The successful execution of this framework, particularly in the initial phases of anticipation and talent creation, requires close collaboration across organizational departments. While HR traditionally leads workforce management, the complexity of megaprojects demands active involvement from operations, strategy, and technical teams in defining future needs and designing appropriate training programs. Operations and technical leaders must work closely with HR and training partners to articulate specific skill requirements, validate training curricula, and ensure programs align with operational realities. This collaborative approach in the early stages creates a strong foundation before transitioning to HR for recruitment execution and ongoing employee management. Such integration helps avoid the siloed approaches identified earlier as a key pitfall, ensuring that workforce development efforts truly meet organizational needs while maximizing resource efficiency.
Case Study: Singapore's Human Capital Excellence
Singapore, a city-state that consistently ranks at the top of the World Bank's Human Capital
In its early years of independence, Singapore's economic planners recognized a competitive edge in the petrochemical industry due to the nation's strategic geographic location, which positioned it as a leading trade hub in Asia. As a result, they strategically focused the development of their higher educational offering around skillsets that catered to this industry. Today, Singapore leverages five-year sectoral economic projections and overlays them with macro and micro trends such as an aging population and automation, to pinpoint roles that will be in high demand.
To close supply-demand gaps, Singapore adopts a dual strategy to attract and cultivate talent. It ensures a robust local talent pipeline by providing higher education institutions with insights into future skill requirements while maintaining openness to immigration in high-skill, high-demand fields such as software engineering. To further develop its workforce, Singapore introduced the 'Skills Future' initiative, which identifies essential behavioural and technical skills across various job families and incentivizes employers to deliver high-quality, hands-on training programs.

Case Study: Cirque du Soleil
As it scaled from 20 street performers in 1984 to a global operation with 4,000
With this strong human capital foundation in place, Cirque du Soleil has been able to deliver its shows to 190M spectators across 450
Setting Up for Success
When implementing human capital strategies, several key enablers help to ensure alignment, scalability, and sustainability:
Governance and Collaboration: Leaders should establish a Human Capital Steering Committee with representation from all relevant departments, including operations, finance, HR, and strategy. Define clear roles and responsibilities and ensure a regular cadence for meetings to maintain alignment and proactively address potential challenges.
Planning: Integrate human capital planning into project milestones. Align workforce readiness efforts with the overall project timeline to ensure timely and seamless recruitment, training, and onboarding.
Technology: Organizations must embrace technology and data-driven solutions. This includes using advanced Human Capital Management (HCM) systems to plan, recruit, and train at scale. Data analytics and AI can optimize workforce forecasting, identify skill gaps, and enhance recruitment and training processes. Digital platforms streamline onboarding, manage talent pipelines, and facilitate continuous learning.
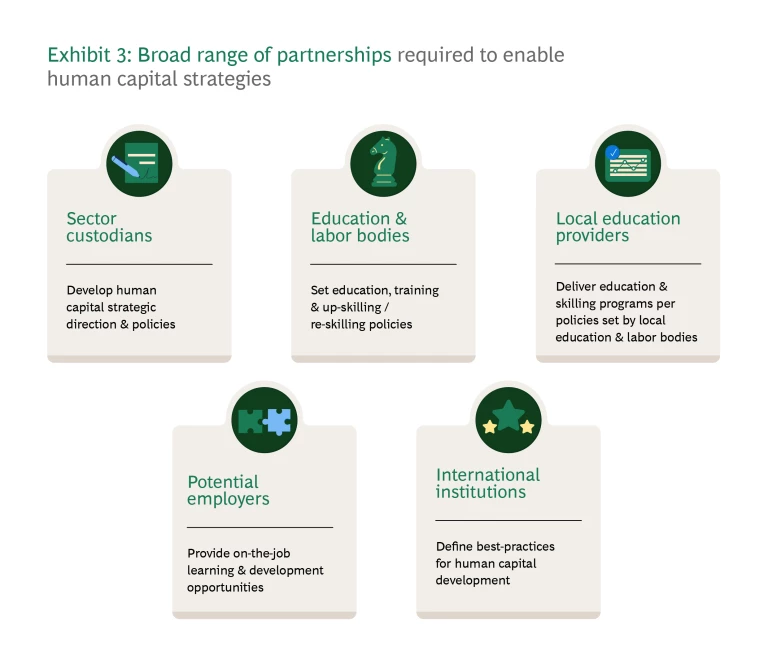
Strategic Partnerships: There is no reason to act in isolation. Collaboration with education and training institutions helps align programs with project needs. Engaging with regulatory bodies ensures compliance with policies like Saudization and adaptation to changing regulations. Partnership with private sector stakeholders builds a robust talent ecosystem that supports long-term workforce sustainability. In Saudi Arabia, collaborating with government entities (such as the National Training Fund) is especially key to aligning talent supply with megaproject needs. By sharing insights on future demand, project leadership can help guide policies that ensure universities and academies are equipped to meet these needs while strengthening the broader talent ecosystem.
Conclusion
Saudi Arabia’s ambitious transformation under Vision 2030 depends on the development of a skilled, future-ready workforce capable of sustaining and driving the Kingdom’s megaprojects. Meeting the workforce challenges—such as talent shortages, competition, and the evolving demands of new sectors—requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach across government, private sector, and education stakeholders.
By implementing a robust human capital strategy that anticipates future needs, develops localized talent, and fosters strategic partnerships, the Kingdom can build a sustainable workforce ecosystem. This foundation will not only ensure the operational success of its megaprojects but also deliver a lasting socio-economic impact that aligns with Saudi Arabia’s bold aspirations






